Therapists and clients collaborate on psychotherapy treatment plan, which are more than documentation. These plans guide therapy goals, interventions, and progress evaluation. Personalized guides encourage collaboration and enable people to actively shape their mental and emotional progress.
Plans are more than sessions which are essential to treatment. They provide guidance, structure, and a customized approach to ensure therapy meets your needs and goals.
Your voice and goals are reflected in these plans, boosting teamwork in your healing path. They stay with you throughout your emotional health journey. These treatment plans are dynamic blueprints for a more balanced and fulfilled existence.
Structured psychotherapy treatment plans are vital. It has various benefits:
- It clarifies therapy goals for therapists and clients.
- Therapy tailored to an individual’s needs addresses their concerns and obstacles.
- Goals and evaluation methods help track progress and adjust treatment.
Psychotherapy Plan Identification
- Therapists assess clients’ psychological, emotional, and behavioral inclinations before starting therapy. A diagnosis helps identify difficulties and establish the best treatment.
- The therapist and client set measurable, achievable goals. The goals track therapy progress.
- Client needs and preferences determine therapy strategies. Examples include psychoanalysis and mindfulness.
- Reviewing goal progress is routine. Change the treatment plan at this stage.
Client-Specific Adult Plans
Life conditions, responsibilities, and development must inform adult treatment. Adult therapy approaches must consider career, relationships, family, and past experiences. A plan that resonates and motivates therapy must also consider cultural background, beliefs, and personal preferences. For more information, visit now.
The Psychotherapy Treatment Plan Development Process
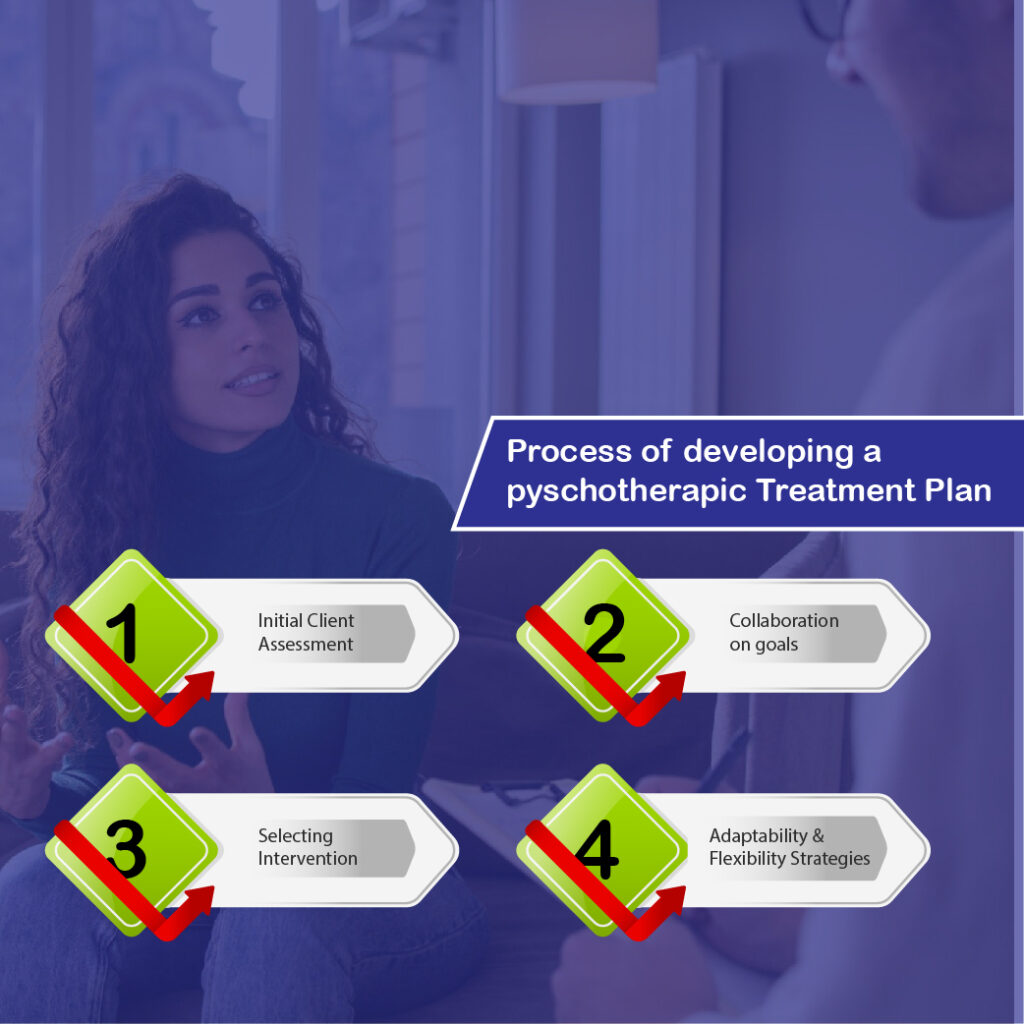
First Client Assessment
A good treatment strategy begins with a client assessment. It involves gathering client history, concerns, therapy goals, and mental health issues. Therapists use interviews, questionnaires, and psychological exams to understand clients.
Goal-Setting Collaboration
Therapy goal-setting involves client-therapist cooperation. It makes goals feasible, meaningful, and client-aligned. Collaboration boosts ownership, drive, and therapy commitment.
Intervention Selection
The therapist picks strategies and approaches to address client needs after assessing and defining goals. Therapy may include conversation, cognitive-behavioral, mindfulness, or exposure. Personality, preferences, and obstacles determine selection.
Strategies for Adaptability and Flexibility
A successful treatment plan acknowledges therapy’s fluidity. Flexibility is needed for client growth, demands, and external influences. To keep treatment effective, therapists should be flexible with goals and approaches.
Essential Adult Psychotherapy Treatment Planner Elements
An Individualized Approach
Treatment must be tailored to the patient. What works for one client may not for another. Customized therapy boosts client engagement.
Calendar and Session Structure
Timing and organizing therapy sessions helps organize and progress. Maintaining momentum and helping the therapist and client track improvement requires consistent sessions, frequency, and duration.
Evidence-Based Methods
Methods based on evidence Implement integrative practices based on research and clinical efficacy. This integration demonstrates that therapy strategies have helped connect issues.
Dealing With Issues
Practical treatment planners anticipate and resolve therapy issues. Options include alternate therapies, ways to handle resistance and setbacks, and plans for tough therapy times.
Executing and Monitoring Treatment Plans
Undertaking and Tracking
Modifications
Treatment approach flexibility facilitates adjustments. Periodic exams help therapists evaluate strengths and deficiencies. Discussing these components with the client helps adapt the plan to their needs.
Client participation in monitoring empowers them. Promote open communication and ask for treatment plan feedback to ensure their voice is heard and improvements are made. Such involvement improves therapy collaboration.
Final Thoughts
A successful psychotherapy treatment plan has many parts. Each element is crucial to success, from assessment and collaborative goal planning to implementation, monitoring, and flexibility in making adjustments.
Therapists and clients follow psychotherapy treatment programs. Personalization, progress tracking, and collaboration boost therapy outcomes.
Developing and implementing a custom treatment plan indicates the therapist’s commitment to the client’s mental and emotional health. Adjusting these programs helps therapists maximize clients’ positive transformation and progress.
Client participation in monitoring empowers them. Promote open communication and ask for treatment plan feedback to ensure their voice is heard and improvements are made. Such involvement improves therapy collaboration.

