LBD is a complex puzzle of cognitive, motor, and behavioral issues. Picture this: Lewy bodies and small protein deposits quietly alter brain activity, causing many problems. Consider lewy body dementia a complicated disorder with two main subgroups: DLB and PDD. Abnormal protein building in these subgroups causes a spectrum of symptoms that fluctuate, making each person’s experience unique. LBD’s intricacy is endless, from acute visual hallucinations to variable awareness and Parkinson ‘s-like movement impairments.
Living with LBD presents several obstacles. It’s the never-ending cognitive rollercoaster, routine uncertainty, and unforeseen behavioral changes. But this complex network of symptoms holds hope and a desire to understand.
Researchers relentlessly investigate this illness to find new answers. From novel pharmaceuticals targeting specific symptoms to cutting-edge diagnostic biomarkers, earlier interventions and individualized care may become the norm.
LBD is more than a diagnosis—it’s a collection of stories, a continuous exploration, and a tribute to human perseverance. We seek understanding, empowerment, and hope on this path.
What Distinguishes LBD?
Cognitive capacities, attentiveness, and awareness vary in LBD. Visual hallucinations, Parkinsonism, and attention fluctuations can mimic Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disorders.
LBD is the third leading cause of dementia after Alzheimer’s and vascular dementia. It accounts for 10-25% of dementia cases. LBD is common, but its symptoms overlap with other neurodegenerative conditions, making it easily misdiagnosed.
Lewy Body Dementia Treatment Challenges: Understanding the Landscape
Due to its complex symptoms and diagnosis, LBD is difficult to treat. A one-size-fits-all therapy approach is complex due to symptom diversity and severity. Hypersensitivity to antipsychotics and other dementia treatments complicates treatment.
Important of a Comprehensive Treatment Plan
LBD requires a multidisciplinary treatment strategy comprising neurologists, psychiatrists, geriatricians, nurses, and caretakers. The method emphasizes symptom management, quality of life, and patient and caregiver support.
Given LBD’s various symptoms, a personalized treatment plan that incorporates illness progression and demands is essential. This may involve medication, non-pharmacological therapies, and caregiver support.
Treatment Options
Drugs For LBD Symptoms
Inhibitors of Cholinesterase
Donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine are often used for LBD cognitive symptoms. They increase neurotransmitters involved in memory and cognition to improve cognition, behavior, and ADLs.
Medications for Parkinson
Levodopa, which treats Parkinson’s disease movement symptoms, can also aid LBD sufferers. Due to adverse effects such as increased hallucinations or confusion, these drugs must be watched.
Non Pharmacological Treatments
- Mental stimulation like Puzzles, reading, and socializing can assist LBD patients in maintaining cognitive function and quality of life.
- Physical activity matched to the individual’s skills can improve motor symptoms and well-being.
- Occupational therapists can help LBD patients adjust their environments and routines for independence and safety.
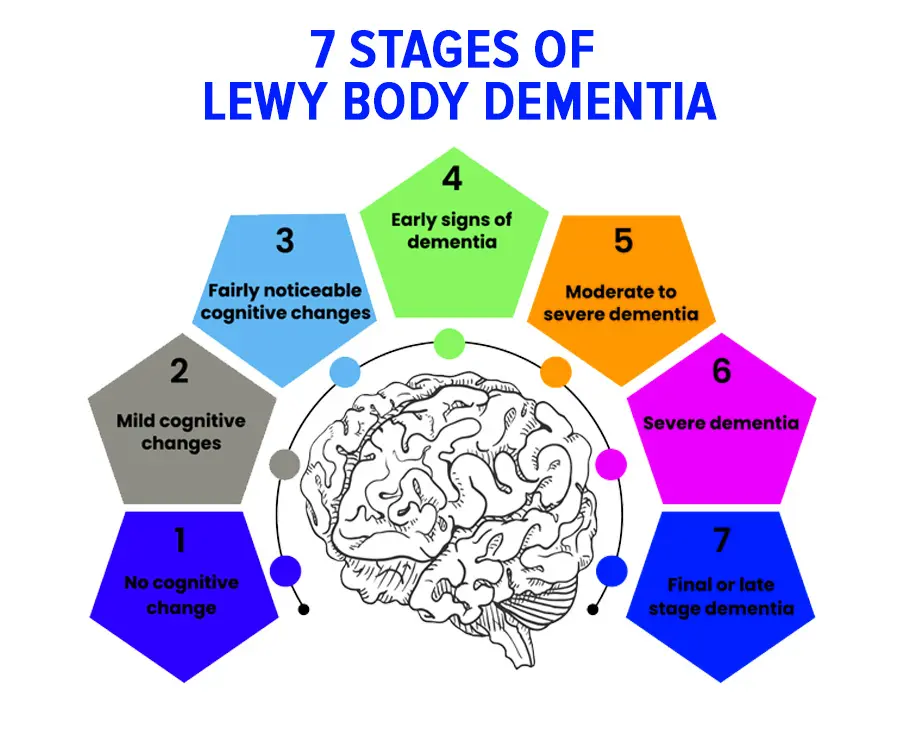
7 Stages of Lewy Body Dementia Treatment
- Stage 1:
Treatment for Early Symptoms Approach: Management of modest cognitive abnormalities may include lifestyle changes, mental activities, and drugs for specific symptoms.
- Stage 2:
Mild Impairment Treatment To improve symptoms, intensifies cognitive stimulation, add caregiver support programs, and considers drugs.
- Stage 3
Moderate Cognitive Decline
- Treatment Approach
Increased cognitive and behavioral issues require more regulated daily routines, advanced caregiver assistance, and medication modifications.
- Stage 4
In advanced Cognitive Decline, the treatment approach prioritizes safety precautions, caregiver involvement, and medication reviews to manage progressively severe symptoms.
- Stage 5
Severe Cognitive Decline Treatment Method: Manages symptoms with 24/7 care and medication modifications to ensure comfort, quality of life, and safety.
End-Stage Decline Treatment Approach: Stage 6
Palliative care, symptom management, and comfort are its primary goals.
- Treatment in Stage 7:
Terminal Phase Approach: Provides dignity, comfort, and respite from stressful symptoms to patients and their families during end-of-life care.
Treatment priorities shift from treating symptoms to improving comfort and quality of life for the patient and caregivers as the disease develops.
For More Information Visit: https://www.brightpoint-md.com/blogs/
Guidelines For Treating Dementia With Lewy Bodies as Recommended by Healthcare Professionals
- Healthcare providers prioritize personalized LBD care strategies based on each patient’s symptoms. These strategies may include medication, treatments, and lifestyle changes.
- Symptoms must be monitored regularly. Healthcare providers urge periodic examinations to evaluate therapy efficacy and make modifications.
- Neurologists, psychiatrists, geriatricians, and other professionals work together to treat LBD holistically, treating cognitive, motor, and behavioral issues.
- Patient and caregiver education is crucial. Understanding disease progression, treating symptoms, and coping strategies improve the quality of life for both partners.
Emerging Therapies and Research
Several promising LBD therapy approaches are being researched. Novel treatments that target LBD symptoms with minimal adverse effects are a priority. These drugs may improve a patient’s quality of life by improving cognition and motor and behavioral symptoms.
Another important aspect of research is biomarker identification. Biomarkers may enable earlier and more accurate diagnosis, faster therapies, and better disease management for LBD patients. Precision medicine may improve LBD management in the future. Personalized LBD treatment based on genetics and illness features may improve outcomes.
Gene therapy, immunotherapy, and deep brain stimulation are also being investigated for LBD treatment. These non-traditional LBD management methods offer hope for better treatments and patient quality of life.
Conclusion
Treatment for Lewy Body Dementia (LBD) is complicated. LBD management involves a comprehensive, customized approach, including symptom-targeted drugs, non-pharmacological therapies, and disease progression.
To treat LBD’s complex symptoms, doctors propose a multidisciplinary team, regular monitoring, and personalized care regimens. Living or caring for someone with LBD can be daunting. Hope remains despite the obstacles. Research advances offer hope for greater understanding, diagnosis, and treatment.
Engaging in exciting activities and following treatment regimens can improve the quality of life for patients. Caregivers receive support from support groups, education programs, and specialized networks. Remember, LBD is difficult, but focusing on what can be handled and the joy and connection that continue is important. Support, education, and taking small steps can help in this road.
FAQ's
LBD is notable for its cognitive fluctuations, vivid hallucinations, and Parkinson ‘s-like movement symptoms. LBD symptoms can change quickly, unlike other dementias.
A thorough medical history, symptoms, and cognitive evaluation are needed to diagnose LBD. LBD’s unique traits must be distinguished from other neurodegenerative illnesses for accurate diagnosis.
Medication for cognitive and motor symptoms, non-pharmacological treatments such as cognitive stimulation, physical exercise, and occupational therapy, and a multidisciplinary care team for tailored care plans are typical.
Beginning with moderate cognitive abnormalities, LBD progresses to severe cognitive impairment and end-stage. Adjusting to illness progression, treatment aims to move from symptom management to comfort and quality of life.
Improved drugs with fewer side effects, biomarker discovery for early diagnosis, and precision medicine are being studied. Future gene and immunotherapy treatments for LBD may also improve symptoms.

